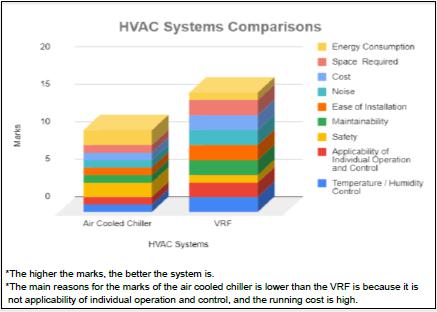
Figure 1 HVAC Systems Comparisons
In order to reduce the energy consumption of commercial buildings, our team used various parameters (temperature and humidity control, applicability of individual operation and control, safety, maintainability, ease of installation, noise, cost, and installation space required) to analyze and compare three common air conditioning systems in Hong Kong which included air-cooled chillers, window type air conditioner and variable-refrigerant-flow (VRF) equipment.
Our research concluded that the VRF system with a dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) is the best option for commercial buildings. Although commercial buildings can benefit more with VRF system as compared with the other two systems, refrigerant safety must also be considered. Since the VRF system distributes refrigerant to conditioned areas rather than using water or air as a means of heat removal, it requires more refrigerant comparatively than the chiller system. According to ASHRAE standard 15 - Safety Standard for Refrigeration Systems, VRF is a “direct” and “high probability of leakage” system, so it has been designed in accordance with the requirements of the relevant standards, such as adding refrigerant leakage detectors and the refrigerant charge limits stipulated in the Standard to ensure safety.

Figure 1 HVAC Systems Comparisons
Figure 2 3D Layout (Typical Floor - Commercial Building)
< Back